About Knowledge Management
The description of Knowledge Management is divided into the following sections:
- What is Knowledge Management?
- Status Handling
- Create Knowledge Article
- Article Handling
- Display Knowledge Article
- Feedback
What is Knowledge Management?
Knowledge Management is the capability to create, manage, display, and provide feedback on Knowledge Articles. These articles can be written to provide details on how to solve a specific issue, how to troubleshoot an object, or any other kind of knowledge suitable for sharing. The Knowledge Management capability within the service is compatible with Request Management.
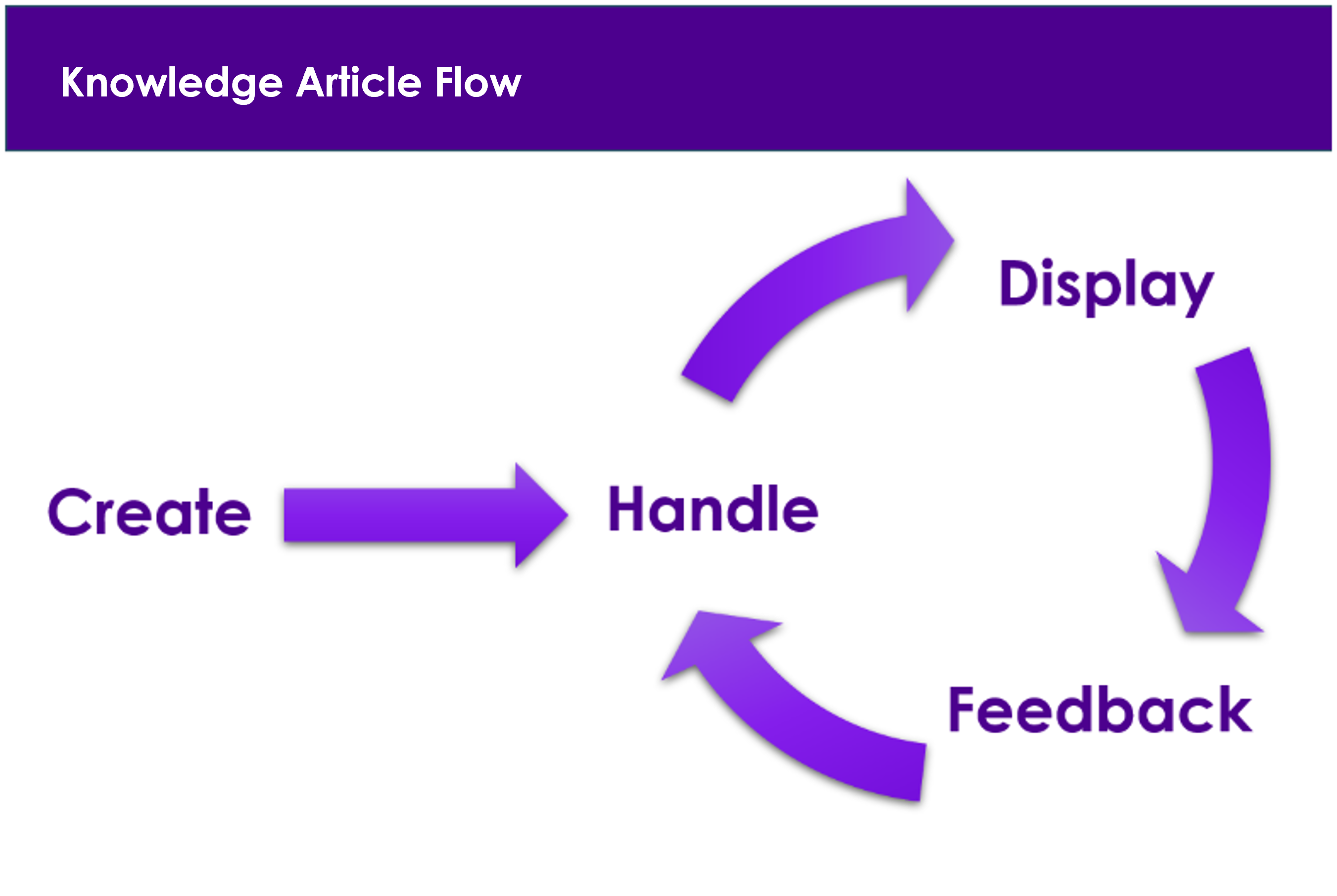
The flow of a knowledge article throughout its lifetime is as follows:
- Creation: This can occur in one of two ways: manually or from a completed Request Work Task.
- Handling: Ensure the content of the article is correct before it is displayed and used as a reference in different contexts.
- Display: Present relevant information in appropriate situations.
- Feedback: Ensure the content remains up to date and of the best possible quality.
This is how the Knowledge Management article flow in simple:
Status Handling
- Draft: The initial state of the knowledge article. In the draft state, the content can be changed without creating a new revision.
- Sent for Approval: When the article creator is satisfied with the content, it can be sent for approval. If the article is rejected, it will revert to Draft. If approved, the status changes to Approved.
- Approved: Once an article is approved, a summary can be generated. To edit the content of approved and published articles, a new revision must be created. To ensure the article is visible as a suggested article, its status must be changed to Published.
- Published: Only published articles are displayed as suggestions.
- Obsolete: When the content of an article is no longer relevant, it can be set to Obsolete, This ensures it is no longer displayed as a suggestion. Articles are automatically set to Obsolete when a new revision is created.
Create Knowledge Article
Article Template
An article template can be used to create the basic structure of a knowledge article. including mapping a layout with predefined headers and providing descriptive text on what information should be added under each header. It is also possible to set a predefined title, select categories, and define visibility.
Structure of AI Generated Article
To ensure that knowledge articles are created uniformly, a predefined structure can be created, where headers are added, their order defined, and the expected information specified under
each header.
The quality of generated knowledge articles may vary when using the Structure of AI Generated Article. The sections included in the article can be defined in the nested table. The order
determined by the Order No and the Description specifying the expected content under each section. This structure provides additional context to guide the AI in generating structured and relevant content.
Manually Create Knowledge Article
Knowledge articles can be created manually or, if needed, using a template. To ensure that knowledge sharing is focused on sharing knowledge, improvement suggestions of the layout, improving grammar, and reducing minor spelling errors can be performed in this stage.
Generate Knowledge Article from Request Work Task
When work is performed, a knowledge article can be generated based on the information entered when the Request was created, along with the details reported in the Request Work Task. During this process, both the content and the title are automatically generated. Since the generation relies on the input provided in the Request and Request Work Task, the quality of the article depends heavily on the quality of the details entered. Both the title and content can be edited before the record is created. The content will be generated in markdown format and can be edited accordingly.
An approval template can be added at this stage and sent for approval during creation.
Depending on the details available in the Request Work Task, different tags will be associated with the article. For example, if only Customer, Location, and Service are defined, neither Object nor Model will be stored as tags. The tags that can be stored are:
- Customer
- Location
- Object
- Model
- Service
Article Handling
To ensure the content is correct and of sufficient quality to be used as a reference, an approval process can be created. A Person Group can be created for scenarios where multiple people need to review a step in the approval process. If only one person is required to review the article, a single person can be assigned to the step.
More details about Approval Routing can be found here:
Article Summary
When an article is created, a summary can be either manually entered or automatically generated. If generated automatically, an LLM (Large Language Model) will analyze the article’s content, and the generated summary can then be edited.
Display Knowledge Article
A knowledge article can be displayed in different contexts based on the tags associated with it. These articles can appear on the Request Details page and the Request Work Task page.
Feedback
Ratings
A knowledge article can be rated both when it is suggested and directly from the Knowledge Article itself. In addition to the ratings, users can leave comments. These, along with the person who rated it and the timestamp, will be stored with the article.
Revisions
When a new revision of a knowledge article is created, the previous revision is marked as obsolete and will no longer appear as a suggested article.